Table of Contents
- Beta
- How To Invest In Mutual Funds And Grow Your Money For Retirement, A Bucket
- The Sparknotes Take: What Is Volatility?
- Ratios Used In Predicting Stock Prices
- Beta And The Vix
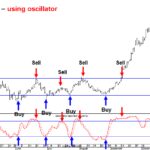
Because beta measures the sensitivity of an asset to the movements of the overall market portfolio, and the market portfolio obviously moves precisely with itself, its beta is one. In quieter markets, a stock may breakout to the upside and lose its momentum, drifting sideways or eventually falling back below the breakout level. However, in a volatile market, where prices are moving rapidly, an upside breakout can be followed by an immediate and substantial run to higher prices. This type of potential is the primary reason to trade breakouts in a volatile market environment. The key to this approach is to find a stock that has been trending higher but which has not yet accelerated the pace of its advance.
In retaliation, Iran threatened to close the Straits of Hormuz, potentially restricting oil supply. Even though the supply of oil did not change, traders bid up the price of oil to almost $110 in March. Kimberly Amadeo is an expert on U.S. and world economies and investing, with over 20 years of experience in economic analysis and business strategy.
Beta
But through Black Monday, the Dot.com Bust, and Great Recession, investors who have panicked and reacted to market volatility are typically the ones who have lost the most potential earnings. The winners have been investors who kept the long-term view in mind and remained calm through volatility. Now that you know what volatility is, how it’s calculated, and what causes it, the next step is to continue living your life and investing in a way that will help you reach your financial goals. So, should you invest in low-volatile stocks and bonds or high-volatile stocks? The correct answer is a combination of both, depending on your age, goals, and risk tolerance. This can be done by dividing the stock’s current closing price by the previous day’s closing price, then subtracting 1.
- First, we provide paid placements to advertisers to present their offers.
- After watching this video lesson, you will learn how the return on equity helps you as a potential investor determine whether a certain company is worth investing in or not.
- The compensation we receive from advertisers does not influence the recommendations or advice our editorial team provides in our articles or otherwise impact any of the editorial content on Forbes Advisor.
- Earnings volatility refers to how stable, or unstable, the earnings of a corporation are.
- Every year, it gets back to 70/30, and this is the basis of how most smart index fund strategies work.
- On any given day, the market as a whole will rise or fall — sometimes by only a few points and other times by hundreds of points.
The emotional status of traders is one reasonwhy gas prices are often so high. Extreme weather, such as hurricanes, can send gas prices soaring by destroying refineries and pipelines. For example, resort hotel room prices rise in the winter, when people want to get away from the snow. They drop in the summer, when vacationers are content to travel nearby. That is an example of volatility in demand, and prices, caused by regular seasonal changes. Price volatility is caused by three of the factors that change prices.
How To Invest In Mutual Funds And Grow Your Money For Retirement, A Bucket
It is effectively a gauge of future bets investors and traders are making on the direction of the markets or individual securities. Volatility often refers to the amount of uncertainty or risk related to the size of changes in a security’s value. A higher volatility means that a security’s value can potentially be spread out over a larger range of values. This means that the price of the security can change dramatically over a short time period in either direction. A lower volatility means that a security’s value does not fluctuate dramatically, and tends to be more steady.

– The difference between a stock’s return and the market’s return. Join the new premium research service for timely deep-dive analysis of high-conviction investment opportunities. The CAPE ratio of the S&P 500 is one measure of how highly valued the price of the market is compared to the value of the market. In trying to replicate scenario four in particular, no portfolio manager or individual investor will be able to get it right every time. Backtesting like this is interesting but it’s not necessarily instructive on how to proceed going forward.
The Sparknotes Take: What Is Volatility?
Down Capture measures how much performance loss a fund captures relative to a benchmark index in down markets. Up Capture measures how much performance gain a fund captures relative to a benchmark index in up markets. Earnings are the amount of profit that a company produces during a specific period. Book Value is the value of a security or asset as entered in a company’s books.
What is volatile anger?
Volatile Anger
People with intermittent explosive disorder have episodes of aggressive, violent behavior or angry verbal outbursts that are grossly out of proportion to the situation.
A stop-loss order is another tool commonly employed to limit the maximum drawdown. In this case, the stock or other investment is automatically sold when the price falls to a preset level.
Ratios Used In Predicting Stock Prices
The advantage of using beta is that it is useful way to gauge an asset’s volatility in relation to the overall stock market. The disadvantage of using beta is that it is based on historical data and may not necessarily be an accurate predictor of future volatility. The Charles Schwab Corporation provides a full range of brokerage, banking and financial advisory services through its operating subsidiaries. Its broker-dealer subsidiary, Charles Schwab & Co., Inc. , offers investment services and products, including Schwab brokerage accounts. Its banking subsidiary, Charles Schwab Bank , provides deposit and lending services and products.
One measure of the relative volatility of a particular stock to the market is its beta (β). A beta approximates the overall volatility of a security’s returns against the returns of a relevant benchmark (usually the S&P 500 is used). For example, a stock with a beta value of 1.1 has historically moved 110% for every 100% move in the benchmark, based on price level. Conversely, a stock with a beta of .9 has historically moved 90% for every 100% move in the underlying index. There are several ways to measure volatility, including beta coefficients, option pricing models, and standard deviations of returns. Volatility is a statistical measure of the dispersion of returns for a given security or market index.
Watch Now: How To Invest In A Volatile Market And Tips For Riding Out The Roller Coaster
Volatility is a statistic that measures the differences between returns of an investment over a given time period – a greater difference means greater volatility. Generally, the higher the volatility, the more risky an investment is considered to be. Note that volatility refers both to positive and negative moves, but the nature of markets is such that negative moves typically occur more dramatically than positive moves . Stock market volatility is a measure of how much the stock market’s overall value fluctuates up and down; beyond the market as a whole, individual stocks can be considered volatile as well. More specifically, you can calculate volatility by looking at how much an asset’s price varies from its average price.
For example – some have sector constraints, meaning that they must maintain at least some exposure to each sector at all times. So, if one sector is particularly volatile, that may result in a higher volatility stock being included in the portfolio over a lower volatility stock in a different sector. Factors are measurable characteristics of a security that help explain its performance. The Low Volatility factor applies to the stocks that have been the least volatile in their asset class over time — avoiding the sharper ups and downs of other stocks. Learn more about this factor with our Low Volatility 101 resource. A common method of calculating the relative volatility of a security to the market is its beta.
By extension, that also means there’s only a 32% chance the stock will be outside this range. 16% of the time it should be above $60, and 16% of the time it should be below $40.
Historically, the S&P 500’s long-term average standard deviation has been 15.6 percent, according to Adviser Investments. For example, in 2017, standard deviation went as low as 6.7 percent, the second-lowest level since 1957. (The lowest year on record was 1963 when standard deviation was just about 5 percent.) And the S&P moved by 1 percent or more on only nine trading days that year. So in 2018, when volatility returned to the historic average, those “normal” levels were jarring to many investors. After all, the roller-coaster ride that is the stock market can be pretty scary for the faint of heart and many novice investors. Market volatility is measured by finding the standard deviation of price changes over a period of time.
How Implied Volatility Can Help You Estimate Potential Range Of Movement On A Stock
Because it is implied, traders cannot use past performance as an indicator of future performance. Instead, they have to estimate the potential of the option in the market. Implied volatility , also known as projected volatility, is one of the most important metrics for options traders. As the name suggests, it allows them to make a determination of just how volatile the market will be going forward. One important point to note is that it shouldn’t be considered science, so it doesn’t provide a forecast of how the market will move in the future.
So here’s a quick and dirty formula you can use to calculate a one standard deviation move over the lifespan of your option contract — no matter the time frame. But for now, let’s stay focused on the implied volatility of the at-the-money option contract for the expiration month you’re planning to trade. Because it’s typically the most heavily traded contract, the at-the-money option will be the primary reflection of what the marketplace expects the underlying stock to do in the future. So you’ll generally see variances in implied volatility at different strike prices and expiration months. In Meet the Greeks, you’ll learn about “vega”, which can help you calculate how much option prices are expected to change when implied volatility changes. Conversely, if implied volatility decreases after your trade is placed, the price of options usually decreases.
Derived from the price inputs of the S&P 500index options, it provides a measure of market risk and investors’ sentiments. Because people tend to experience the pain of loss more acutely than the joy of gain, a volatile stock that moves up as often as it does down may still seem like an unnecessarily risky proposition. However, what seasoned traders know that the average person may not is that market volatility actually provides numerous money-making opportunities for the patient investor. Each trade carries with it the risk both of failure and of success. Volatility is also used to price options contracts using models like Black-Scholes or binomial tree models. More volatile underlying assets will translate to higher options premiums, because with volatility there is a greater probability that the options will end up in-the-money at expiration.
It disproportionately benefits from market recoveries while preserving capital better when stocks fall. In addition to buying businesses with wide economic moats, the second critical thing for reducing risk is to buy at a price that is at or below the fair value of the investment. To do that, you need to apply discounted cash flow analysis or a similar valuation technique that’s based on the actual value that the company produces. When market volatility reaches a certain level, things can start to move so quickly that closer attention and a change in tactics may be necessary. The steps discussed in this article are no guarantee to keep you on course, but are worthwhile to consider if you think you’re ready to take on volatile markets.